In the world of industrial piping, selecting the right type of Spiral Pipe can significantly impact the success of a project. An esteemed expert in the field, Dr. John Smith, a mechanical engineer with over two decades of experience, emphasizes the importance of this decision with his statement: "Choosing the right Spiral Pipe is not merely a preference; it's a necessity that influences efficiency and safety." This highlights that understanding the fundamental characteristics of Spiral Pipes is crucial for any construction or manufacturing endeavor.
When embarking on a project that involves Spiral Pipes, one must consider several critical factors, including material choice, pipe diameter, and intended application. These elements play a pivotal role in determining the overall performance and longevity of the piping system. For instance, different materials offer varied resistance to corrosion and pressure, which could directly affect the operational integrity of a project. By following essential guidelines, project managers and engineers can ensure that their choice of Spiral Pipe is aligned with both functional demands and safety standards, paving the way for a successful outcome.

When selecting the right spiral pipe for your project, it’s crucial to understand the different types available and their specific applications. Spiral pipes are typically categorized based on their manufacturing processes and material compositions. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, each offering unique benefits. For instance, while carbon steel is durable and cost-effective, stainless steel is preferred for projects requiring superior corrosion resistance.
Another important aspect to consider is the diameter and wall thickness of the spiral pipes, which can significantly impact their performance in various applications. Smaller diameter pipes are often used for residential projects and low-pressure systems, while larger diameters are better suited for industrial applications requiring higher pressure capacity. Additionally, the type of spiral construction—whether it's single or double welding—plays a role in the strength and reliability of the pipe. Understanding these variations will enable you to choose the most suitable spiral pipe for your specific needs, ensuring efficiency and longevity in your project.
When selecting spiral pipes for a project, understanding the material options available is crucial, as each type offers distinct benefits. Among the most common materials are steel, stainless steel, and plastic. Steel spiral pipes are renowned for their strength and durability, making them ideal for high-pressure applications, particularly in industrial settings. Their resilience ensures they can withstand harsh environmental conditions while maintaining structural integrity.
On the other hand, stainless steel provides additional corrosion resistance, which is beneficial in environments exposed to moisture or corrosive substances. This material is often preferred in food processing and chemical industries due to its hygienic properties. Conversely, plastic spiral pipes present a lightweight alternative, featuring excellent chemical resistance and easy installation, which can be advantageous for smaller-scale projects or in residential applications. Each material choice comes with its advantages, making it essential to assess the specific requirements of your project to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the spiral pipes selected.
| Material Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Strength, cost-effective, good for high-pressure applications | Susceptible to corrosion | Construction, oil and gas transportation |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant, durability, aesthetic appeal | Higher cost | Food processing, pharmaceuticals, chemical industries |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, resistant to corrosion, good thermal conductivity | Lower strength compared to steel | HVAC systems, marine applications |
| PVC | Low cost, resistant to chemical corrosion, lightweight | Not suitable for high-temperature applications | Drainage systems, plumbing |
| Fiberglass | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good for thermal insulation | Brittle, can be expensive | Chemical processing, piping for industrial applications |
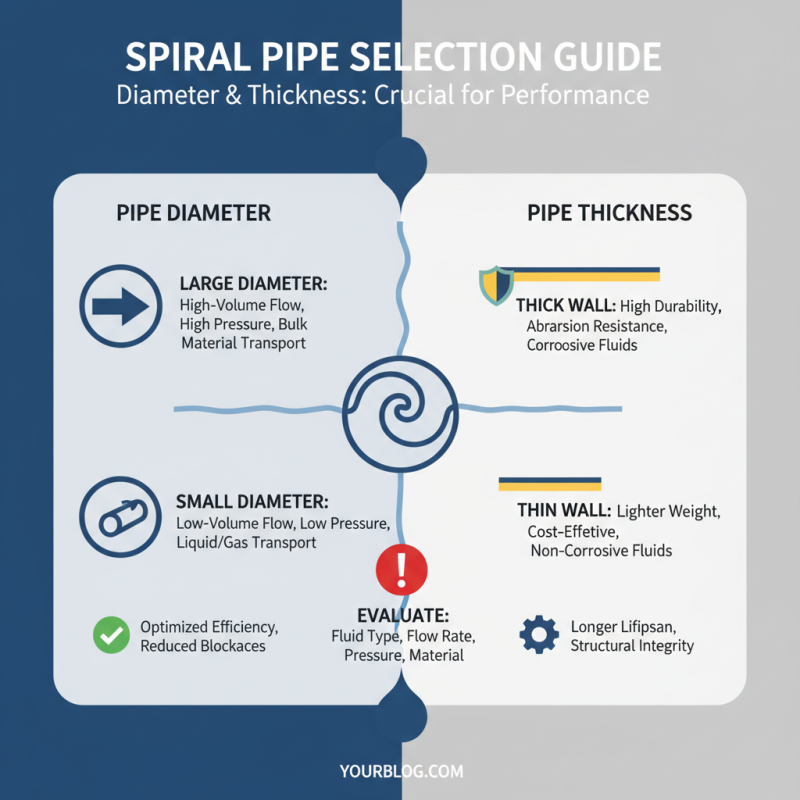
When selecting a spiral pipe for your project, evaluating the diameter and thickness is crucial to ensure optimal performance and durability. The diameter of the pipe should align with the specific requirements of your application, considering factors such as fluid flow rates, pressure levels, and the type of material being transported. Larger diameters may be necessary for high-volume applications, while smaller diameters can be suitable for low-flow systems. Ensuring the right diameter will not only enhance efficiency but also minimize the risk of issues like turbulence and potential blockages.
Thickness is equally important as it directly impacts the pipe’s structural integrity and resistance to external pressures or corrosive elements. For projects exposed to harsh environments or significant weight loads, selecting a thicker pipe is advisable to ensure longevity and reliability. Conversely, in less demanding applications, a thinner pipe might suffice, offering cost savings without sacrificing performance. Consideration of both diameter and thickness should be based on a thorough assessment of your specific conditions, ensuring that the spiral pipe meets all operational requirements while remaining within budget constraints.
When choosing the right spiral pipe for your project, the selection of pipe coating and corrosion resistance options is crucial to ensure durability and longevity. The environment in which the pipe will be installed significantly influences the type of coating you should consider. For instance, if the pipe will be exposed to moisture or harsh chemicals, you may want to opt for coatings that provide enhanced resistance to corrosion. Epoxy and polyurethane coatings are popular choices, as they create a protective barrier against corrosive elements while also providing excellent adhesion and flexibility.
Additionally, it is essential to understand the various corrosion resistance options available. Galvanization, for example, involves coating the pipe with a layer of zinc, which serves as a sacrificial barrier to protect the underlying metal from corrosion. This method is particularly effective in environments prone to rust. Alternatively, stainless steel options offer inherent corrosion resistance without the need for additional coatings, making them an excellent choice for projects where high strength and resistance to corrosion are paramount. Evaluating these factors will help you select a spiral pipe that meets both the technical requirements and the environmental challenges of your specific application.
When selecting a spiral pipe for your project, adherence to industry standards and regulations is paramount. Compliance not only ensures safety and reliability but also helps in maintaining the quality of the final output. Different industries have specific standards, such as those set by ASTM, ASME, or ISO, which govern material specifications, dimensions, and performance criteria. Familiarizing yourself with these standards can prevent costly mistakes and rework down the line.
In addition to national or international standards, local regulations must also be taken into account. These can include environmental guidelines, installation codes, and safety practices that are specific to your region or the nature of your project. Engaging with professionals in the field and consulting design specifications can provide valuable insights into regulatory frameworks that affect the choice of spiral pipes. By prioritizing compliance, you not only enhance the integrity of your project but also build a reputation for quality and safety within your industry.






